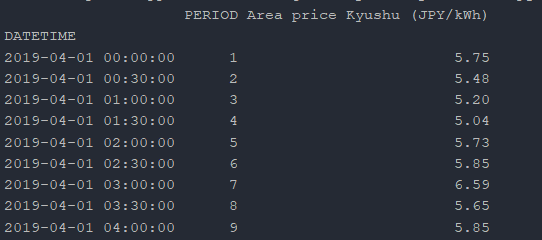
Oftentimes when working with Electricity Market data, you’ll be dealing with CSV files from your sources.
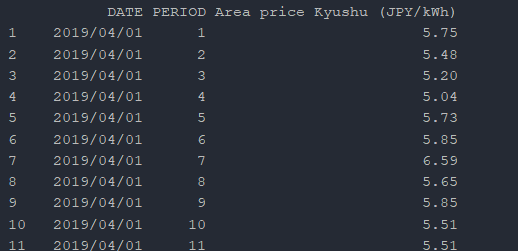
As an example, from the Japanese electricity market (JEPX), the market provides a CSV file with a flat table structure.
In order to use these files as timeseries datasets, further processing is needed to create a time-ordered index. From the JEPX CSV file, there are two columns we can combine to form a time-ordered index: DATETIME and PERIOD.
The function below takes in a pandas dataframe, converts the period as minutes, add the minutes to the target index column, and then converts the target index column into an index.
Function Definition
- Inputs
- df: DataFrame being modified
- targetColumn: Column to be designated as the index, usually datetime
- periodColumn: Column to be combined to the datetime, usually period
- targetColumnFmt: formate of the targetcolumn
- Outputs
- DataFrame - Re-indexed Dataframe with the DateTime column as the index.
- Reference Libraries
- Datetime Timedelta
- Datetime DateTime
from datetime import timedelta
from datetime import datetime
def combineTimePeriodDate(dF,targetColumn='DATETIME',periodColumn='PERIOD',targetColumnFmt ='%Y/%m/%d' ):
for i, row in dF.iterrows():
minutes_add = ((int(dF.at[i, periodColumn]) * 30) - 30)
dF.at[i, targetColumn] = datetime.strptime(dF.at[i, targetColumn], targetColumnFmt) + timedelta(minutes=int(minutes_add))
dF.set_index(targetColumn, inplace=True)
return dF
Result
As a result of the function, the dataframe is returned with a time-ordered index, ready for use.
To-Do
- Allow for hourly, qtrhourly, 5-minute, and 4-hour granularities